School Suspensions Down, But Students of Color, Low Income Receive Disproportionate Share
/There’s good news and bad news in a new analysis of suspensions, expulsions, and arrests of students in Connecticut schools. The report, by Connecticut Voices for Children, found that overall significantly fewer students have been excluded from the classroom in recent years, but that suspension, expulsion and arrest rates were much higher for minority students, special education students, and students from poorer districts.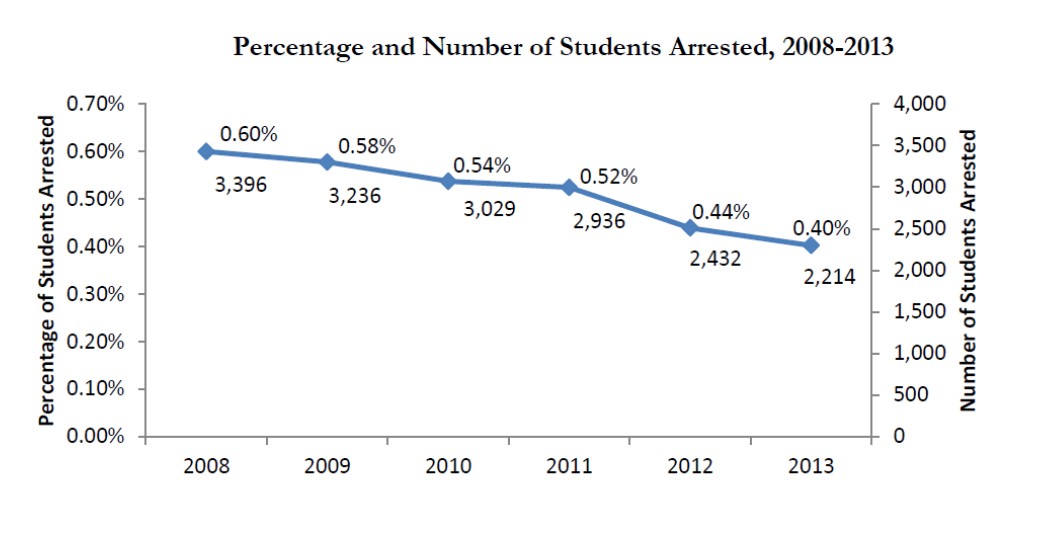 The report also found that “many of these discipline measures were used for behaviors that were probably not criminal and could likely have been handled within the school.” Stressing that “children learn best when they are in school,” the report indicated that “arrests, expulsions, and suspensions are often costly, ineffective, and unnecessary.”
The report also found that “many of these discipline measures were used for behaviors that were probably not criminal and could likely have been handled within the school.” Stressing that “children learn best when they are in school,” the report indicated that “arrests, expulsions, and suspensions are often costly, ineffective, and unnecessary.”
Connecticut Voices for Children is a research and advocacy organization that works to improve opportunities for the state’s children, youth and families. The report, “Keeping Kids in Class: School Discipline in Connecticut, 2008-2013,” uses data provided by local school districts, found that in 2013, 7.4 percent of all students received at least one expulsion or suspension, down from 8.5 percent as recently as 2011.
First, the good news:
- The number of students arrested, expelled, and suspended in Connecticut has decreased significantly in recent years. In the 2013 school year, Connecticut schools arrested 35 percent fewer students, expelled 31 percent fewer students, and gave out of school suspensions to 47 percent fewer students than in 2008.
The not-so-good news:
- Despite the overall reduction in these “exclusionary” school discipline practices, many students are still removed from the classroom for non-criminal behaviors that could, in the view of Connecticut Voices, be managed in the classroom. “School policy violations” – such as skipping class, insubordination, or using profanity – were involved in 9 percent of student arrests, 6 percent of expulsions, 50 percent of out-of-school suspensions, and 79 percent of in-school suspensions in 2013.

From 2008-2013 the percentage of students suspended out-of-school fell from 4.9% to 2.7%. During the same time period, the percentage of students suspended in-school increased from 4.9% to 5.2%.
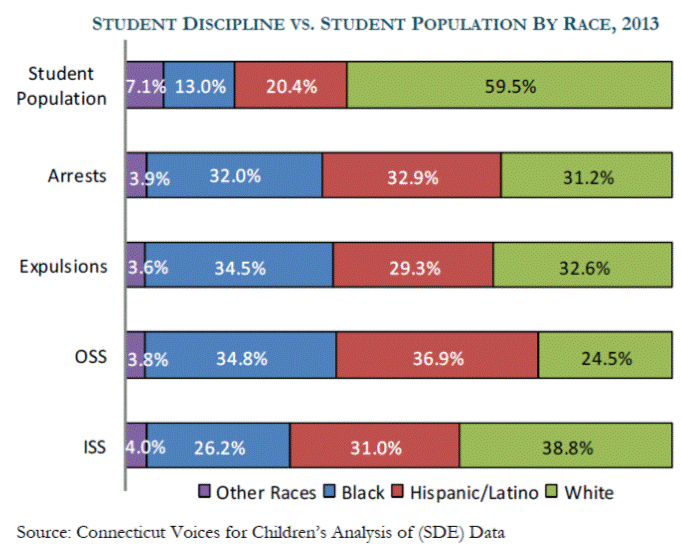
Of particular concern was the data related to students of color and those with limited financial resources or disability:
- In 2013, black students were 4.7 times more likely to be arrested, 4.9 times more likely to be expelled, and 6.5 times more likely to be suspended out-of-school than white students.
- Hispanic students were 3.1 times more likely to be arrested, 2.6 times more likely to be expelled, and 4.4 times more likely to be suspended out-of-school than white students.
- Special education students were arrested at 3 times the rate of general education students, and they were 1.8 times more likely to be expelled, and 2.6 times more likely to receive out-of-school suspensions.
- Students in the poorest urban areas were arrested nearly 23 times more often, expelled over 17 times more often, and suspended out-of-school 24 times more often than students in the wealthiest suburban areas.
Based on the data, the report makes a series of recommendations for the state Department of Education and policymakers to consider, including:
- Require districts with police stationed in schools to create a memorandum of agreement between the schools and police that sets ground rules concerning arrests. Promote police and educator training, such as that provided by the state’s Juvenile Justice Advisory Committee, which offers instruction to officers and educators in understanding and responding productively to adolescent behavior.
- Implement preventive strategies and alternative discipline measures to reduce racial and other disparities and ensure those excluded from school are provided equal opportunities.
- Establish and support community collaborations across the state. National studies show that engaging all stakeholders in the discipline process positively impacts student behavior and achievement.
The top 10 reasons for expulsion in 2013: 1) drug/alcohol/tobacco, 2) weapons, 3) fighting/battery, 4) personally threatening behavior, 5) school policy violations, 6) theft/theft related behaviors, 7) verbal confrontation/conduct unbecoming 8) violent crimes against persons, 9) sexually related behavior, and 10) property damage.
The report concludes that “the disproportionate rate by which students of color and students from poorer districts are excluded from school may in fact contribute to widening the achievement gap; students from less privileged backgrounds will continue to perform worse than their more advantaged peers if they are excluded from the classroom in the first place.”
The report also recommends expanding access to behavioral and mental health services and utilize Juvenile Review Boards (JRBs), locally-run groups that offer a diversionary alternative to the court system for youth who have committed minor delinquent acts or misdemeanors. In addition, it calls for improving data collection by clearly defining “student arrests” (not currently defined by the state) and collecting and publishing data on all student arrests (currently not required for all incidents resulting in arrests).
“This report tells us that many schools in Connecticut have reformed their disciplinary practices and reduced student arrests, expulsions and out-of-school suspensions,” said Ellen Shemitz, Executive Director of Connecticut Voices for Children. “Yet these reforms have not benefited all children equally. How can we hope to reduce the yawning achievement gap when school disciplinary practices push minority children out of school at disproportionate rates?”






 The study also noted that “barriers to accessing community based care among Connecticut Medicaid beneficiaries are well-documented, often leaving such patients with few options other than hospital care for both urgent and non-urgent conditions.”
The study also noted that “barriers to accessing community based care among Connecticut Medicaid beneficiaries are well-documented, often leaving such patients with few options other than hospital care for both urgent and non-urgent conditions.”
 ocations in Connecticut are in Bridgeport, Danbury,
ocations in Connecticut are in Bridgeport, Danbury, 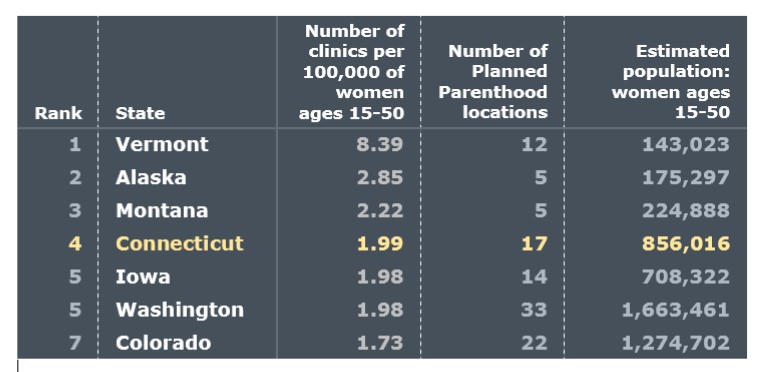
 for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently released new data showing that while cervical cancer screenings have been proven to save lives, about eight million women ages 21 to 65 have not been screened for cervical cancer in the past five years. More than 12,000 women in the U.S. are diagnosed with cervical cancer each year, and more than half of these cases are in women who have never been screened or in those who haven’t been screened in the past five years, according to Planned Parenthood.
for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently released new data showing that while cervical cancer screenings have been proven to save lives, about eight million women ages 21 to 65 have not been screened for cervical cancer in the past five years. More than 12,000 women in the U.S. are diagnosed with cervical cancer each year, and more than half of these cases are in women who have never been screened or in those who haven’t been screened in the past five years, according to Planned Parenthood.

 A home study by a social worker, along with background checks, must be completed before applications will be accepted, and grant awards will be determined by members of a board, based on criteria including need and personal circumstances, such as “why they want to build their family through adoption.” Board members already in place include individuals with backgrounds in finance, law, fundraising, and social work, whose lives have been touched by adoption. Additional board members are now being determined.
A home study by a social worker, along with background checks, must be completed before applications will be accepted, and grant awards will be determined by members of a board, based on criteria including need and personal circumstances, such as “why they want to build their family through adoption.” Board members already in place include individuals with backgrounds in finance, law, fundraising, and social work, whose lives have been touched by adoption. Additional board members are now being determined.
 Denise Morrison, the subject of the lead business story in the February 2, 2015 issue of
Denise Morrison, the subject of the lead business story in the February 2, 2015 issue of 

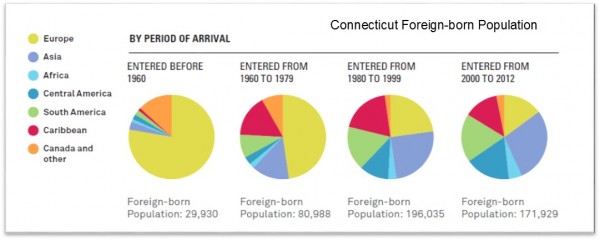
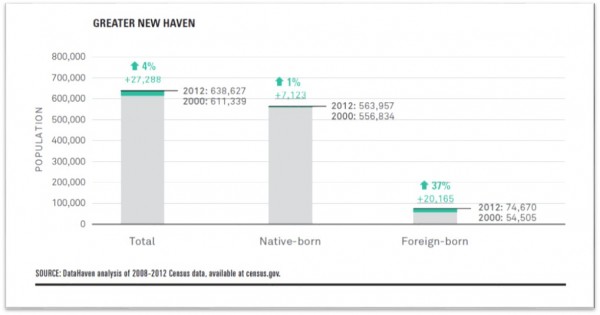 In New Haven’s neighborhoods in particular, the boost in immigrants has revitalized communities and spurred new businesses. From 1970 to 1990, the foreign-born population in most New Haven neighborhoods remained flat or declined, and these neighborhoods suffered from overall population decline—similar to other central city neighborhoods in post-industrial cities. Since 1990, the report found, the foreign-born population in many city neighborhoods has rebounded sharply, particularly in areas such as Edgewood, West River, Fair Haven, and the Hill. These areas have seen a large influx of population and business overall.
In New Haven’s neighborhoods in particular, the boost in immigrants has revitalized communities and spurred new businesses. From 1970 to 1990, the foreign-born population in most New Haven neighborhoods remained flat or declined, and these neighborhoods suffered from overall population decline—similar to other central city neighborhoods in post-industrial cities. Since 1990, the report found, the foreign-born population in many city neighborhoods has rebounded sharply, particularly in areas such as Edgewood, West River, Fair Haven, and the Hill. These areas have seen a large influx of population and business overall.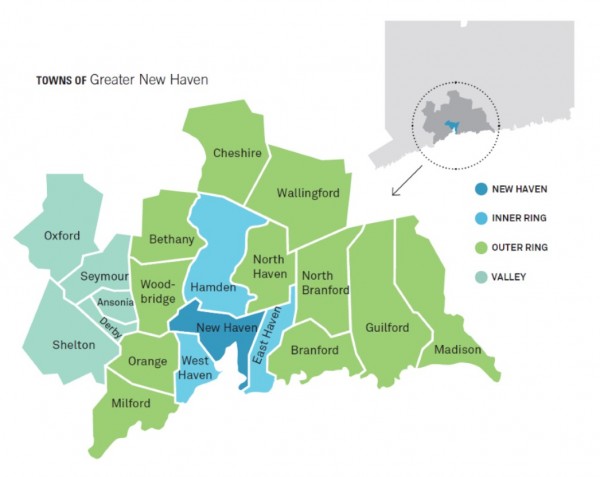



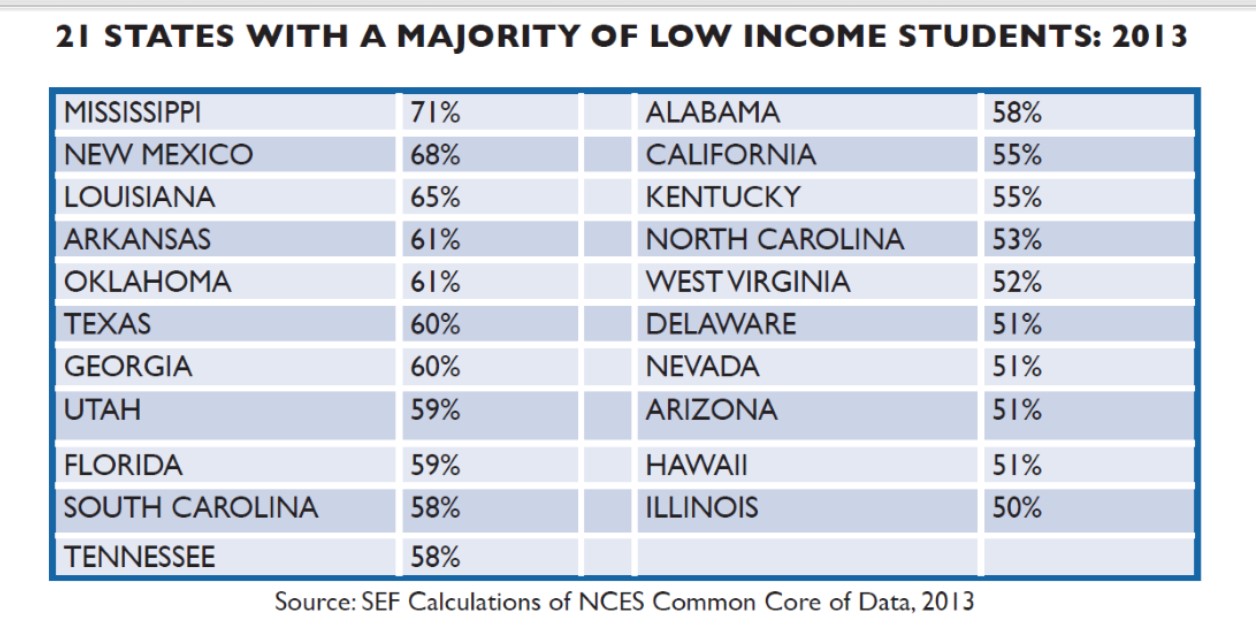 hat “The trends of the last decade strongly suggest that little or nothing will change for the better if schools and communities continue to postpone addressing the primary question of education in America today: what does it take and what will be done to provide low income students with a good chance to succeed in public schools? It is a question of how, not where, to improve the education of a new majority of students.”
hat “The trends of the last decade strongly suggest that little or nothing will change for the better if schools and communities continue to postpone addressing the primary question of education in America today: what does it take and what will be done to provide low income students with a good chance to succeed in public schools? It is a question of how, not where, to improve the education of a new majority of students.”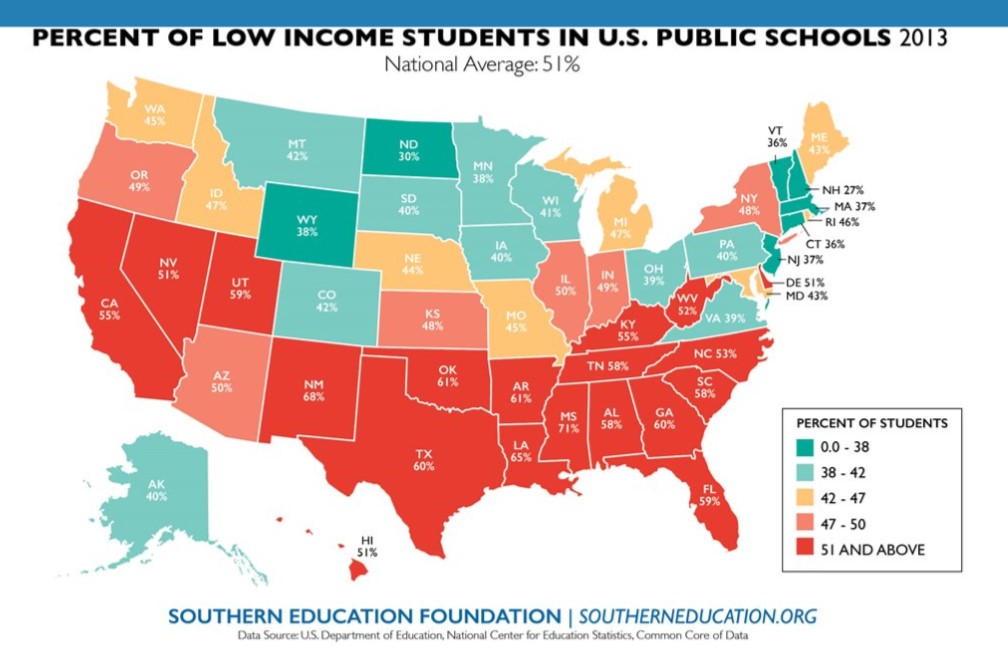
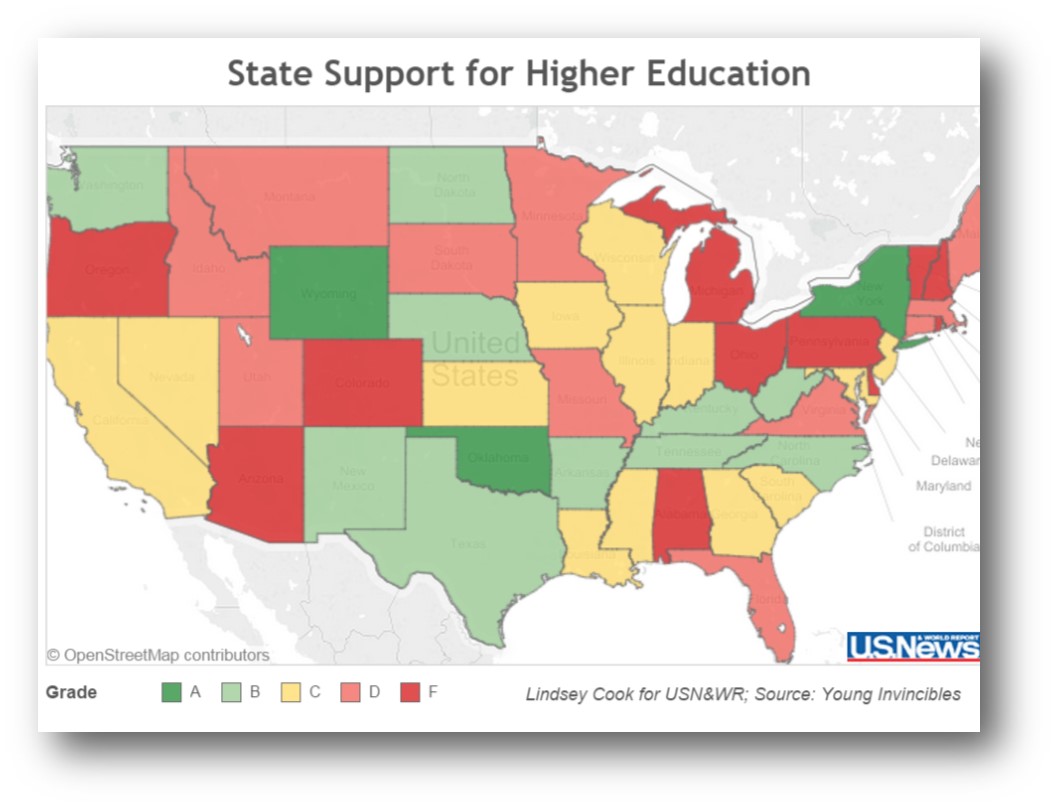
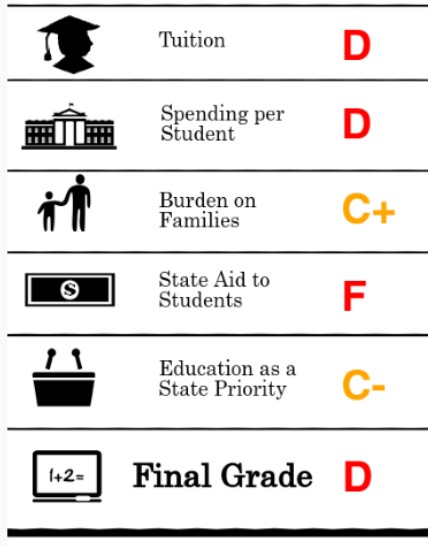 last month by the General Accounting Office in Washington, D.C. for the U.S. Senate found “persistent state budget constraints have limited funding for public colleges” across the country. The result, according to the GAO report: “Students and their families are now bearing the cost of college as a larger portion of their total family budgets.”
last month by the General Accounting Office in Washington, D.C. for the U.S. Senate found “persistent state budget constraints have limited funding for public colleges” across the country. The result, according to the GAO report: “Students and their families are now bearing the cost of college as a larger portion of their total family budgets.”
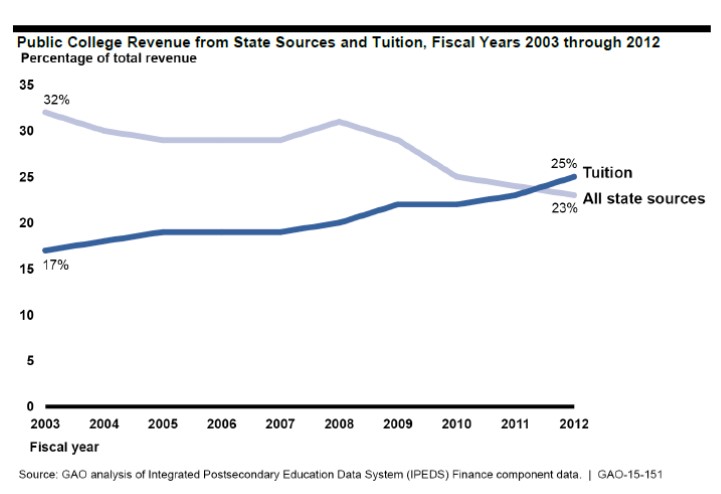 “state grant aid directly affects students in that it can reduce their out-of-pocket expenses for college… state grant aid, both merit- and need-based, has positive effects on enrollment.” The results of one program, in Washington State, cited by GAO “suggests that receiving the aid increased a student’s probability of enrolling in college by nearly 14 to 19 percentage points.”
“state grant aid directly affects students in that it can reduce their out-of-pocket expenses for college… state grant aid, both merit- and need-based, has positive effects on enrollment.” The results of one program, in Washington State, cited by GAO “suggests that receiving the aid increased a student’s probability of enrolling in college by nearly 14 to 19 percentage points.”



























