Greater Hartford Residents Prefer Focus on Vibrant Communities Over Recruiting Businesses
/In a time of reduced resources and stark choices for policy makers, a survey of Greater Hartford residents suggests that investments aimed at creating vibrant communities, with the focus on local schools, transportation options, walkable, attractive physical environment is preferred to devoting greater resources to recruiting employers.
In a survey for the Hartford Foundation for Public Giving as part of the Metro Hartford Progress Points effort, and conducted by Inform CT, residents of Hartford and Tolland County, by 57 percent to 43 percent, said that investing in communities was a better approach than recruiting businesses.
The findings reaffirm one of the key goals in the new three-year strategic plan of HFPG, launched earlier this year, developing vibrant communities. The plan states that “All of our region’s residents should have the opportunity to live and contribute to strong, safe vibrant communities,” and calls for a “focus on people and places with the greatest need by engaging and supporting partners who promote meaningful civic engagement, safe affordable housing, quality health and mental health care and a rich diversity of cultural and other experiences to improve the quality of life.”
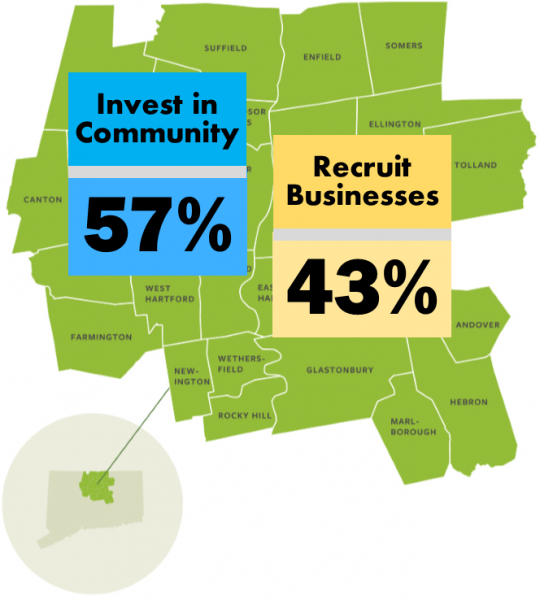 The data from the survey reflect a difference of opinion among older residents of the region. Individuals over age 46 took the opposite view from younger residents, with a majority expressing a preference for spending skewed toward recruiting companies. The reversal was dramatic, with two-thirds of those age 36-45 preferring investing in communities, by a margin of 67%-33%, and individuals age 46-55 expressing a preference for resources to be aimed at recruiting companies, with two-thirds holding the opposite view, 63%-38%.
The data from the survey reflect a difference of opinion among older residents of the region. Individuals over age 46 took the opposite view from younger residents, with a majority expressing a preference for spending skewed toward recruiting companies. The reversal was dramatic, with two-thirds of those age 36-45 preferring investing in communities, by a margin of 67%-33%, and individuals age 46-55 expressing a preference for resources to be aimed at recruiting companies, with two-thirds holding the opposite view, 63%-38%.
Across all age groups, a majority of homeowners preferred that the emphasis be on vibrant communities, 52%-48%, and an even larger majority of respondents who are not homeowners, 64%-36%, shared the same view.
The preference for policy to be targeted more towards assuring vibrant communities than recruiting companies was consistent across a majority of respondents of various education levels and among white, black and Hispanic residents of the region, according to the survey. A majority of survey respondents who are currently employed full-time, as well as those working part-time, and those unemployed all expressed a preference for investing in communities rather than recruiting companies.
The Greater Hartford survey results are not inconsistent with data gathered elsewhere. A March 2014 national survey by the American Planning Association (APA) found that Millennials and Baby Boomers want cities to focus less on recruiting new companies and more on investing in new transportation options, walkable communities, and making the area as attractive as possible. The national survey found that 65 percent of all respondents and 74 percent of millennials believe investing in schools, transportation choices and walkable areas is a better way to grow the economy than investing in recruiting companies to move to the area, according to the APA.
A 2013 study in Michigan, posing similar questions, brought similar results. In the statewide survey, 64 percent of Michigan citizens said they believed the most important thing state government can do for job creation is to “provide quality education, good roads and transportation, good public services like safety, water, fire, parks and libraries that create an environment in which people want to live, work and run a business.” This contrasts with 29 percent who said the most important thing state government can do is to “cut taxes for individuals and businesses.”
Earlier this month, at the annual Municipal Collaboration Summit organized by the Hartford Business Journal, one of the session’s was devoted to an exploration of “Building Vibrant Communities,” with observations from representatives of Connecticut Main Street Center, the Partnership for Strong Communities and the Connecticut Economic Resource Center.
The Hartford Foundation for Public Giving serves 29 towns, hundreds of nonprofits and more than 750,000 residents in the Greater Hartford region. As Greater Hartford’s community foundation, HFPG brings together members of the community to “share information, understand local problems and put resources behind effective solutions.”
Developed by a group of key regional stakeholders, Metro Hartford Progress Points is a periodic 'check-up' to build greater understanding about issues facing the Greater Hartford community. The second edition of Progress Points, released late last year, takes a deeper look at key issues impacting our communities and how they are connected, with a particular focus on access to better schools, better jobs and stronger neighborhoods. Along with the Hartford Foundation, partners include the Hispanic Health Council, MetroHartford Alliance, United Way of Central and Northeastern Connecticut, Urban League of Greater Hartford, Capitol Workforce Partners, Capitol Region Council of Governments, the Center for Urban and Global Studies at Trinity College and the City of Hartford.
The survey was conducted for the Foundation during the 4th quarter of 2015 by Inform CT.


 Chinese made up 35 percent of the 92,000 foreign secondary school students in the United States in 2015, according to the US Department of Homeland Security, by far the largest group studying here, the Boston Globe
Chinese made up 35 percent of the 92,000 foreign secondary school students in the United States in 2015, according to the US Department of Homeland Security, by far the largest group studying here, the Boston Globe 




 In Connecticut, a person is guilty of trafficking in persons when such person compels or induces another person to engage in sexual contact or provide labor or services by means of force, threat of force, fraud or coercion. Anyone under the age of 18 engaged in commercial sexual exploitation is deemed a victim of domestic minor sex trafficking irrespective of the use of force, threat of force, fraud or coercion.
In Connecticut, a person is guilty of trafficking in persons when such person compels or induces another person to engage in sexual contact or provide labor or services by means of force, threat of force, fraud or coercion. Anyone under the age of 18 engaged in commercial sexual exploitation is deemed a victim of domestic minor sex trafficking irrespective of the use of force, threat of force, fraud or coercion. The need for stronger action is underscored by recent statistics. In Connecticut, one of every three kindergartners is overweight or obese, as is one of every three low-income children. Children who are overweight or obese are more likely, according to the policy brief, to have:
The need for stronger action is underscored by recent statistics. In Connecticut, one of every three kindergartners is overweight or obese, as is one of every three low-income children. Children who are overweight or obese are more likely, according to the policy brief, to have: A number of the proposals have been successfully implemented in other jurisdictions, including states and cities. Marlene Schwartz, Director of UConn's Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity, noted that Connecticut has long been a leader in providing nutritional lunches in schools, and said that now the state’s attention needs to move to the earlier years of childhood. “The field has realized that we need to start even earlier,” she said. Rudd also indicated that determining "policy changes that might help reduce the disparities" in Connecticut, which are apparent in race, ethnicity and socioeconomic data, is also essential.
A number of the proposals have been successfully implemented in other jurisdictions, including states and cities. Marlene Schwartz, Director of UConn's Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity, noted that Connecticut has long been a leader in providing nutritional lunches in schools, and said that now the state’s attention needs to move to the earlier years of childhood. “The field has realized that we need to start even earlier,” she said. Rudd also indicated that determining "policy changes that might help reduce the disparities" in Connecticut, which are apparent in race, ethnicity and socioeconomic data, is also essential.
 The recommendations, described as “affordable, achievable, common sense measures,” were prepared for CHDI as part of a grant to the UConn Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity, funded by the Children’s Fund of Connecticut. The author was public health policy consultant Roberta R. Friedman, ScM.
The recommendations, described as “affordable, achievable, common sense measures,” were prepared for CHDI as part of a grant to the UConn Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity, funded by the Children’s Fund of Connecticut. The author was public health policy consultant Roberta R. Friedman, ScM. IMPACT “Preventing Childhood Obesity: Maternal-Child Life Course Approach” in 2014. The report reviewed scientific research on the causes of obesity and explored implications for prevention and early intervention. In 2015, the Children’s Fund of Connecticut funded four obesity prevention projects in Connecticut that addressed health messaging, data development, policy development and baby-friendly hospitals.
IMPACT “Preventing Childhood Obesity: Maternal-Child Life Course Approach” in 2014. The report reviewed scientific research on the causes of obesity and explored implications for prevention and early intervention. In 2015, the Children’s Fund of Connecticut funded four obesity prevention projects in Connecticut that addressed health messaging, data development, policy development and baby-friendly hospitals.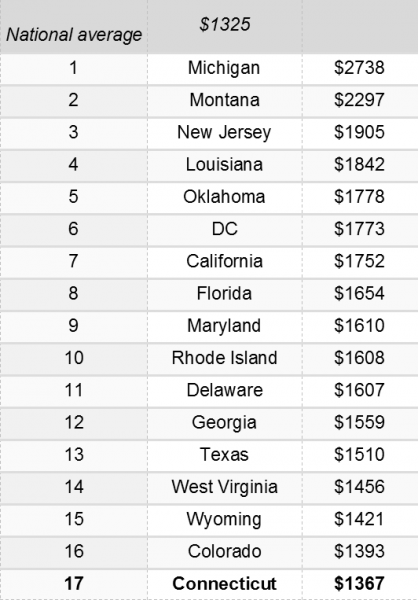
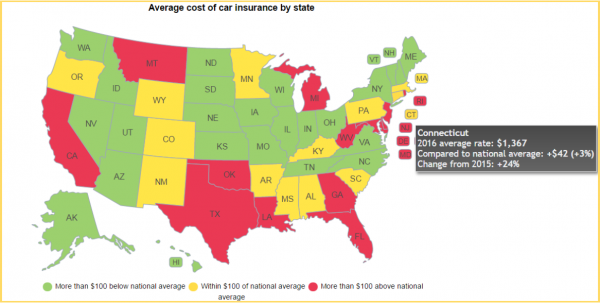 The national average for a full-coverage policy as featured in the Insure.com report came in at $1,325 this year – a slight increase from last year’s average of $1,311. Rates varied from a low of $808 a year in Maine to a budget-busting $2,738 in Michigan. Insurance rates in Michigan are more than double (107 percent) the national average.
The national average for a full-coverage policy as featured in the Insure.com report came in at $1,325 this year – a slight increase from last year’s average of $1,311. Rates varied from a low of $808 a year in Maine to a budget-busting $2,738 in Michigan. Insurance rates in Michigan are more than double (107 percent) the national average.
 ucation systems positively, the lowest percentages in the country, in a
ucation systems positively, the lowest percentages in the country, in a  State residents were asked “how would you rate the quality of public education provided in grades K-12” on a scale including excellent, good, fair and poor. The top 10 states after North Dakota, Minnesota and Nebraska are Iowa, New Hampshire and Massachusetts (80%), Wyoming (79%), South Dakota (78%) and Vermont and Virginia (75%).
State residents were asked “how would you rate the quality of public education provided in grades K-12” on a scale including excellent, good, fair and poor. The top 10 states after North Dakota, Minnesota and Nebraska are Iowa, New Hampshire and Massachusetts (80%), Wyoming (79%), South Dakota (78%) and Vermont and Virginia (75%).


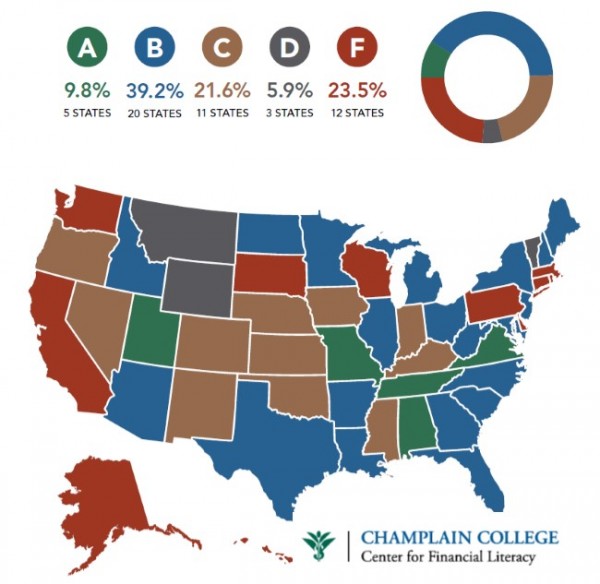 s a comprehensive look into the state of K-12 economic and financial education in the United States, collecting data from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. The biennial Survey of the States serves as an important benchmark, revealing “both how far we’ve come and how far we still have to go.” This year the report concluded that nationally “the pace of change has slowed.”
s a comprehensive look into the state of K-12 economic and financial education in the United States, collecting data from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. The biennial Survey of the States serves as an important benchmark, revealing “both how far we’ve come and how far we still have to go.” This year the report concluded that nationally “the pace of change has slowed.”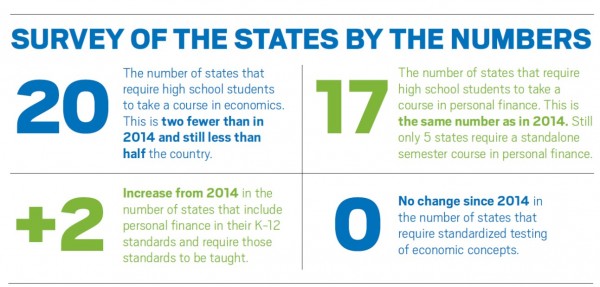 nts accountable for learning objectives have the best chance of promoting the development of young people who are better financial managers and stewards of their credit—behaviors with which many, if not most, young people tend to struggle,” said J. Michael Collins of the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Center for Financial Security. “Rigorous state standards can facilitate local schools to implement well-designed programs, which in turn expose students to concepts they otherwise would not learn.”
nts accountable for learning objectives have the best chance of promoting the development of young people who are better financial managers and stewards of their credit—behaviors with which many, if not most, young people tend to struggle,” said J. Michael Collins of the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Center for Financial Security. “Rigorous state standards can facilitate local schools to implement well-designed programs, which in turn expose students to concepts they otherwise would not learn.” The new network would dramatically extend televised and online coverage and “on-demand access” to all legislative hearings and debates, as well as public policy conferences, regulatory hearings, executive agency meetings, and state Supreme Court and Appellate judicial proceedings.
The new network would dramatically extend televised and online coverage and “on-demand access” to all legislative hearings and debates, as well as public policy conferences, regulatory hearings, executive agency meetings, and state Supreme Court and Appellate judicial proceedings. Giguere pointed out that “there are 10 hearing rooms, but CT¬N’s physical plant limits us to covering only two events concurrently. That means up to 80% of the Legislative committee process at any given time goes unseen. Our capacity to cover the Executive and Judicial Branches is even more limited.”
Giguere pointed out that “there are 10 hearing rooms, but CT¬N’s physical plant limits us to covering only two events concurrently. That means up to 80% of the Legislative committee process at any given time goes unseen. Our capacity to cover the Executive and Judicial Branches is even more limited.” currently funded, CFOG notes, “the new entity would be monitored and accountable to the public, but independent from government itself.”
currently funded, CFOG notes, “the new entity would be monitored and accountable to the public, but independent from government itself.”



























