Connecticut Agriculture Growth Gains National Attention
/Connecticut may be the third smallest state in the nation, but it has a large agricultural presence - which led to the state being featured recently by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) on the federal agency’s website.
Bucking the national trend, USDA reports, Connecticut farming has been growing for the past two decades. The state - based on the 2012 Census of Agriculture - has nearly 6,000 farms, which is a remarkable 60 percent increase from the 3,754 farms in Connecticut in 1982. At the same time, the state’s farmland acreage remained relatively stable, which means that the size of an average farm has been trending down, to an average of 73 acres.
More than 900 Connecticut farms harvested vegetables for sale in 2012, with bell peppers being the most popular crop. To meet the needs of East Coast homeowners and landscapers, in 2012, 880 of Connecticut's nurseries, greenhouses, floriculture and sod farms grew and sold almost $253 million worth of those crops.
In addition, Connecticut’s coastal area has hosted shellfish farms since Colonial times. In 2012, the state’s aquaculture industry sold nearly $20 million worth of seafood, primarily shellfish from Long Island Sound. There is livestock as well, USDA notes, with 774 farms in Connecticut raising cattle and calves. Most of the sales on the livestock end come from milk, however. In 2012, the state’s farms sold nearly $70 million worth of milk from cows.
Contrary to history and stereotype, in 2012 more than 25 percent of all Connecticut farms were operated by women as principal operators. That is an incremental increase from 23 percent in 2007. Overall, the 2012 Census counted more than 3,700 women farmers in the state.
Connecticut farmers have also stepped up their efforts to get agricultural products into consumers’ hands, the USDA report indicated. With the growing “buy local” movement, nearly a quarter of Connecticut farms market human food products directly to consumers. About 10 percent of the farms in the state now market their products directly to retail outlets such as restaurants, stores, and institutions; and at the same time, 218 of our farms participate in community-supported agriculture programs allowing local residents to partake in their harvest.
Although the USDA did not specifically mention the longstanding “Connecticut Grows” campaign from the state’s Department of Agriculture, it has served as a lynchpin for intensified efforts using technology.
The CT Grown Program was developed in 1986, during the administration of former Gov. William A. O’Neill, when the now-familiar green and blue logo was created to identify agricultural products grown in the state. During nearly three decades, the CT Grown Program has blossomed into a multifaceted campaign that promotes these products through a diverse array of avenues in local, regional, national and international markets.
It now features CT Grown producer listings and brochures, connections to farmers markets, the CT Seafood Council, CT Farm Wine Development Council, CT Food Policy Council, CT Milk Promotions Board, and other related councils and commissions.
More recently, the website www.buyctgrown.com was established as “a place to connect people who are ready to discover CT Grown foods and experience Connecticut agriculture.” buyCTgrown is a program of the non-profit CitySeed and receives support from our partners including UConn Extension, CT Farm Bureau, CT NOFA, and the CT Department of Agriculture. 
The website’s “CT 10% Campaign” asks people to spend 10 percent of their existing food and gardening dollars on locally grown goods.” Individuals and businesses can sign up to “take the pledge” on the website, and will receive ongoing information about locally grown products.


 vable Communities
vable Communities rcent, with less than 2 percent growth for people age 20 to 64 during the same period.
rcent, with less than 2 percent growth for people age 20 to 64 during the same period.

 asier to walk and bike by implementing "complete streets" in cities and towns across Connecticut. Complete streets make it easier and safer for people to get around on foot or by bike, in order to become more physically active.
asier to walk and bike by implementing "complete streets" in cities and towns across Connecticut. Complete streets make it easier and safer for people to get around on foot or by bike, in order to become more physically active. ut the
ut the  nd Connecticut Coalition of Mutual Assistance Associations. The project was also supported by the Asian American Studies Institute at UConn, the UConn School of Pharmacy and the UConn School of Social Work. It focused on housing, education, language access, employment, access to public resources, and medical and mental health.
nd Connecticut Coalition of Mutual Assistance Associations. The project was also supported by the Asian American Studies Institute at UConn, the UConn School of Pharmacy and the UConn School of Social Work. It focused on housing, education, language access, employment, access to public resources, and medical and mental health. Healthcare Concerns
Healthcare Concerns d education, promoting preventative care, actively recruiting APA members in various professional fields, creating diversity in the workforce, translating materials into the most common APA languages, and raising awareness among the APA population regarding their rights.
d education, promoting preventative care, actively recruiting APA members in various professional fields, creating diversity in the workforce, translating materials into the most common APA languages, and raising awareness among the APA population regarding their rights.


 In addition, it calls for creation of a consent form for parents of student athletes to sign on the warning signs, symptoms and treatment of SCA and relevant school policies. Similar legislation has already been adopted in Pennsylvania, several other states are also considering SCA bills, according to the SCAF. The provisions of the new law take effect a year from now, with the school year that begins in the fall of 2015.
In addition, it calls for creation of a consent form for parents of student athletes to sign on the warning signs, symptoms and treatment of SCA and relevant school policies. Similar legislation has already been adopted in Pennsylvania, several other states are also considering SCA bills, according to the SCAF. The provisions of the new law take effect a year from now, with the school year that begins in the fall of 2015. Raising Expectations 2014: A State Scorecard on Long-Term Services and Supports for Older Adults, People with Physical Disabilities, and Family Caregivers – an update of the inaugural 2011 Scorecard –
Raising Expectations 2014: A State Scorecard on Long-Term Services and Supports for Older Adults, People with Physical Disabilities, and Family Caregivers – an update of the inaugural 2011 Scorecard –  lex medical tasks – so that their loved ones don’t end up back in the hospital and can continue to live independently at home, according to AARP officials.
lex medical tasks – so that their loved ones don’t end up back in the hospital and can continue to live independently at home, according to AARP officials. “When it comes to helping older Connecticut residents live in the setting of their choice, this silent army of family caregivers assumes the lion’s share of responsibility,” explains Duncan. “Many juggle full-time jobs with their caregiving duties; others provide 24/7 care for their loved ones. With every task they undertake, these family caregivers save the state money by keeping their loved ones out of costly nursing homes – most often paid for by Medicaid. They have earned some basic support.”
“When it comes to helping older Connecticut residents live in the setting of their choice, this silent army of family caregivers assumes the lion’s share of responsibility,” explains Duncan. “Many juggle full-time jobs with their caregiving duties; others provide 24/7 care for their loved ones. With every task they undertake, these family caregivers save the state money by keeping their loved ones out of costly nursing homes – most often paid for by Medicaid. They have earned some basic support.”
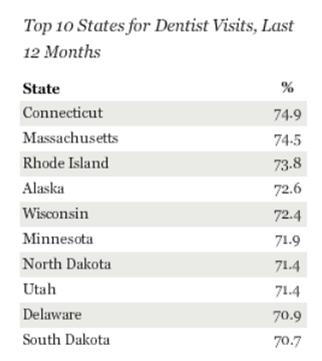
 These findings are based on interviews with more than 178,000 American adults conducted during 2013 as a part of the Gallup-Healthways Well-Being Index. Respondents were asked whether they visited the dentist in the last 12 months.
These findings are based on interviews with more than 178,000 American adults conducted during 2013 as a part of the Gallup-Healthways Well-Being Index. Respondents were asked whether they visited the dentist in the last 12 months.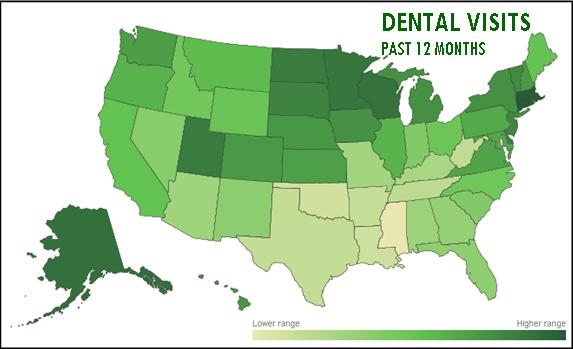

 e rankings is the Washington, D.C., metro area with a score of 77.3, followed by Minneapolis-St. Paul, Portland, Denver, San Francisco, San Jose, Seattle, San Diego, Boston Sacramento and Salt Lake City.
e rankings is the Washington, D.C., metro area with a score of 77.3, followed by Minneapolis-St. Paul, Portland, Denver, San Francisco, San Jose, Seattle, San Diego, Boston Sacramento and Salt Lake City.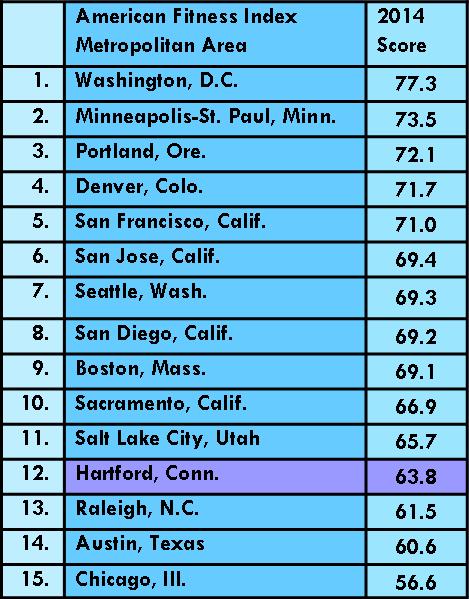 Hartford-East Hartford
Hartford-East Hartford In health outcomes, Tolland County led the way, followed by 2)Fairfield County, 3)Middlesex County, 4)Litchfield County, 5)New London County, 6)Hartford County, 7)Windham County and 8)
In health outcomes, Tolland County led the way, followed by 2)Fairfield County, 3)Middlesex County, 4)Litchfield County, 5)New London County, 6)Hartford County, 7)Windham County and 8)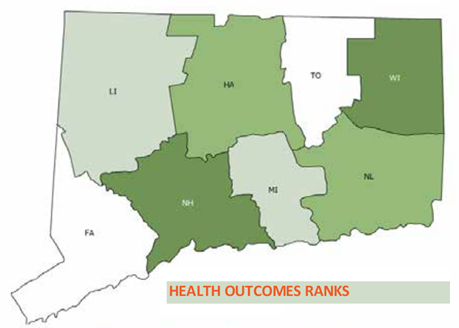 New Haven County.
New Haven County.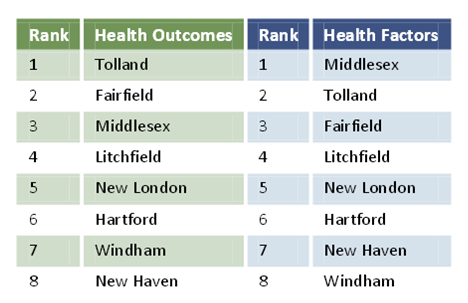
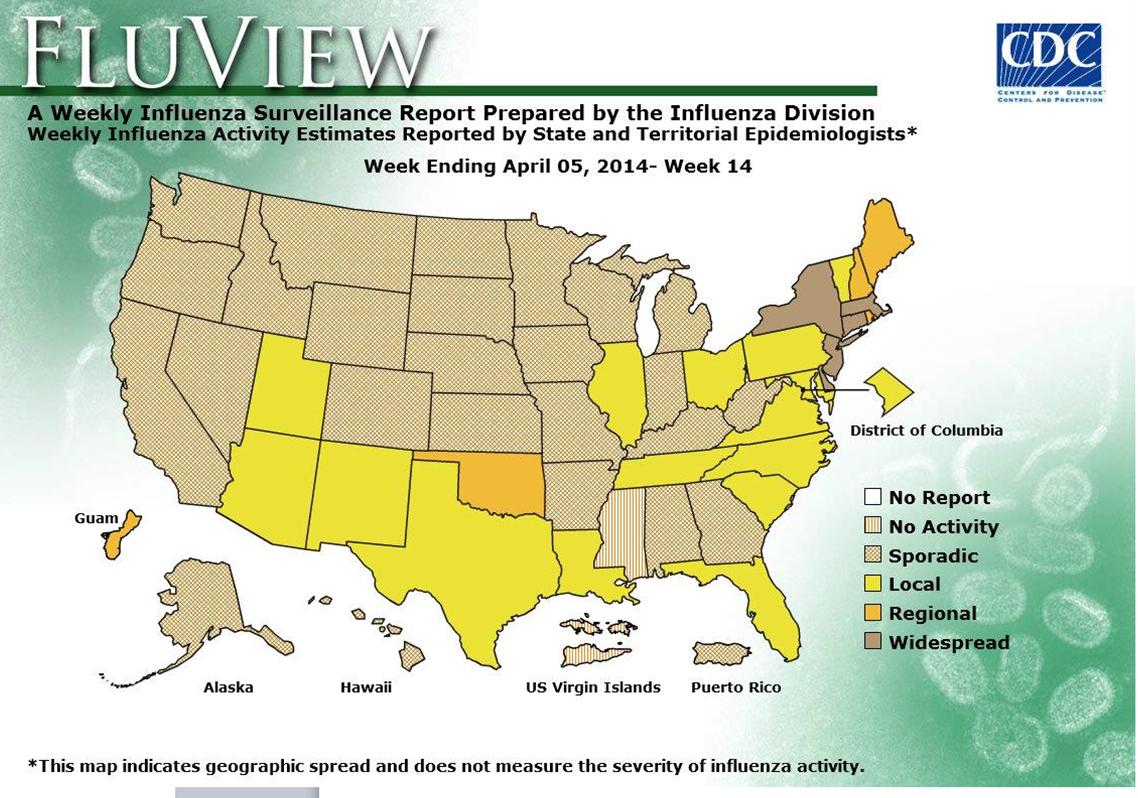
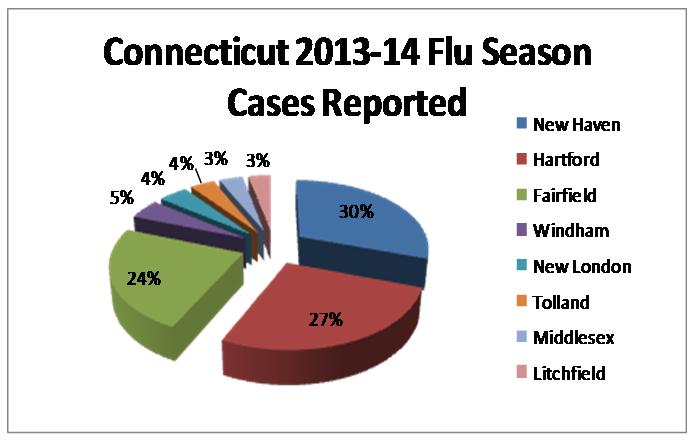 Connecticut is joined by regional neighbors New York, Massachusetts, New Jersey and Delaware in the recent spike in flu cases.
Connecticut is joined by regional neighbors New York, Massachusetts, New Jersey and Delaware in the recent spike in flu cases.