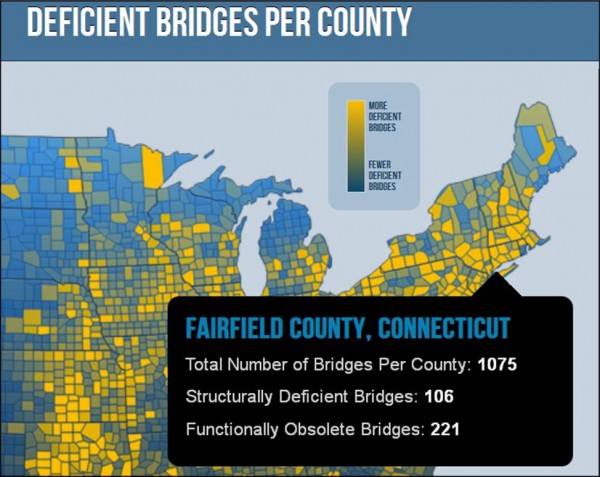
Stereotypes about a thriving and problem-free Asian Pacific population in Connecticut are just plain wrong, according to a new statewide Needs Assessment Study which reveals “high rates of physical and mental health problems” and serious concerns about access to proper food and healthcare, often exacerbated by communication breakdowns and language barriers."
The 21-page study, by the Connecticut Asian Pacific American Affairs Commission, is said to be the first of its kind in Connecticut. The 2010 U.S. Census reported APA’s as one of the fastest growing minority populations, growing from 2.4 percent of Connecticut’s population in 2000 to 4.4 percent by 2010. The Census projects a steady increase of the APA population through 2050.
The Needs Assessment was developed in collaboration with three community-based organizations: the Khmer Health Advocates, Lao Association of Connecticut a nd Connecticut Coalition of Mutual Assistance Associations. The project was also supported by the Asian American Studies Institute at UConn, the UConn School of Pharmacy and the UConn School of Social Work. It focused on housing, education, language access, employment, access to public resources, and medical and mental health.
nd Connecticut Coalition of Mutual Assistance Associations. The project was also supported by the Asian American Studies Institute at UConn, the UConn School of Pharmacy and the UConn School of Social Work. It focused on housing, education, language access, employment, access to public resources, and medical and mental health.
More than 300 Southeast Asian Connecticut residents – all over age 18 - participated in the study, include just over one hundred from each of three ethnic groups: Cambodian, Lao, and Vietnamese. The study found clear distinctions between the populations in Connecticut, and researchers stressed that viewing the Asian Pacific American (APA) population in the state as one block of people does a disservice to them, and does not adequately respond to their needs.
Food Insecurity
Food insecurity was a “prominent problem,” according to the report. “Close to half reported that they often or sometimes couldn’t afford to eat balanced meals and 43 percent indicated that their food supplies ran out The survey also reviewed “several measures of food insecurity” and found “significant association” between the ethnic groups and “finding it too expensive to have a balanced meal often or sometimes,” as well as “going hungry for lack of sufficient money for food.”
The report also indicated that “all of the ethnic groups reported concern that some members of their community were socially isolated. In particular, they reported that those age 50 and older were most at risk for isolation.”
 Healthcare Concerns
Healthcare Concerns
Regarding healthcare, “nearly half experienced at least some difficulty in getting the healthcare they believed they needed,” the report indicated. In addition, “more than half of all participants reported experiencing a language barrier with their physician, and for those that needed an interpreter, 59 percent indicated that a professional interpreter was never or rarely available for healthcare visits.”
In regards to Southeast Asian Refugees, the report noted "chronic mental and physical health conditions follwoing a history of severe trauma," adding that "it is vital that primary care physicians and others treating these individuals screen for a wide range of physical health conditions as well as PTSD and depression." At a State Capitol news conference releasing the report, Dr. Megan Berthold, Assistant Professor in the UConn School of Social Work, said that there is an "urgent need" to address these concerns, adding that the lack of communication can be "dangerous" and could "lead to misdiagnosis."
Among those who received prescriptions, nearly one-third said they did not fill it due to the expense, and among all surveyed, 17 percent “did not see a doctor when they felt they need to” during the past year due to the high cost.
Among the ethnic differences, a greater number of Vietnamese are smokers, Cambodians were “significantly more likely to be diagnosed with PTSD and depression,” and the Lao community indicating the least frequency of language barriers with physicians. Overall, however, the report indicated that “these communities continue to be underserved due to the limited to no resources available to focus on the cultural and linguistic needs of their communities.”
Numerous Recommendations
Included in the recommendations, the study report states that “service providers, state agencies and stakeholders are encouraged to partner with APA communities” in multiple ways, and calls for additional research that “can advance the needs of the APA population.” The series of 14 recommendations include greater training an d education, promoting preventative care, actively recruiting APA members in various professional fields, creating diversity in the workforce, translating materials into the most common APA languages, and raising awareness among the APA population regarding their rights.
d education, promoting preventative care, actively recruiting APA members in various professional fields, creating diversity in the workforce, translating materials into the most common APA languages, and raising awareness among the APA population regarding their rights.
It is hoped that Needs Assessment studies can focus on other APA ethnic groups, such as the Indian and Chinese communities, in future years. The APA population in Connecticut includes approximately 50 ethnic groups, sharing some similarities and having great diversity. As the initial study demonstrated, specific needs may vary – an important fact for policy makers and those working with this fast-growing aspect of the state’s population.
Among those commenting on the report during the news conference were Secretary of the State Denise Merrill, who was instrumental in the establishment of the Commission when she was House Majority Leader in the legislature, Marie Spivey, Chair of the State Commission on Health Equity, Tanya Hughes, Executive Director of the state's Commission on Human Rights and Opportunities, and Dr. William Howe, Chair of the Asian Pacific American Affairs Commission (see photo, at left). Theanvy Kuoch, Executive Directo of Khmer Health Advocates, noted that "working together we can improve outcomes for our community members while engaging them in their own care. We have evidence that this approach also saves health care dollars."
The Asian Pacific American Affairs Commission was created in 2008 by an act of the Connecticut legislature. The 21 member bipartisan commission oversees matters concerning hte Asian Pacific American population in Connecticut, and makes recommendations to the General Assembly and the Governor on the health, safety, education ,economic self-sufficiency and efforts to remain free of discrimination within the APA population in the state.
 tates according to their tendency to produce the highest or lowest monthly energy bills.
The analysis points out that “lower prices don’t always equate with lower costs, as consumption is a key determinant in the total amount of an energy bill.” Connecticut’s monthly energy cost for consumers, according to the analysis, is $404, ranking the state 49th out of 51 (the 50 states plus the District of Columbia). Mississippi’s total monthly cost paid by consumers averages $414, while Hawaii’s is $451.
tates according to their tendency to produce the highest or lowest monthly energy bills.
The analysis points out that “lower prices don’t always equate with lower costs, as consumption is a key determinant in the total amount of an energy bill.” Connecticut’s monthly energy cost for consumers, according to the analysis, is $404, ranking the state 49th out of 51 (the 50 states plus the District of Columbia). Mississippi’s total monthly cost paid by consumers averages $414, while Hawaii’s is $451. the highest in the nation. (see breakdown below)
the highest in the nation. (see breakdown below)



 reas such as New York, Philadelphia, Chicago, Boston, Atlanta, and Washington.
reas such as New York, Philadelphia, Chicago, Boston, Atlanta, and Washington. s median gross apartment rent of $948.
s median gross apartment rent of $948.
 ould be the best fit
ould be the best fit




 vable Communities
vable Communities rcent, with less than 2 percent growth for people age 20 to 64 during the same period.
rcent, with less than 2 percent growth for people age 20 to 64 during the same period.
 nd Connecticut Coalition of Mutual Assistance Associations. The project was also supported by the Asian American Studies Institute at UConn, the UConn School of Pharmacy and the UConn School of Social Work. It focused on housing, education, language access, employment, access to public resources, and medical and mental health.
nd Connecticut Coalition of Mutual Assistance Associations. The project was also supported by the Asian American Studies Institute at UConn, the UConn School of Pharmacy and the UConn School of Social Work. It focused on housing, education, language access, employment, access to public resources, and medical and mental health. Healthcare Concerns
Healthcare Concerns d education, promoting preventative care, actively recruiting APA members in various professional fields, creating diversity in the workforce, translating materials into the most common APA languages, and raising awareness among the APA population regarding their rights.
d education, promoting preventative care, actively recruiting APA members in various professional fields, creating diversity in the workforce, translating materials into the most common APA languages, and raising awareness among the APA population regarding their rights.

 tion, Mamoun’s, Prime 16, Skappo, Bella’s Care and Da Legna.
tion, Mamoun’s, Prime 16, Skappo, Bella’s Care and Da Legna.