PERSPECTIVE: Clearing A Path to Better Health
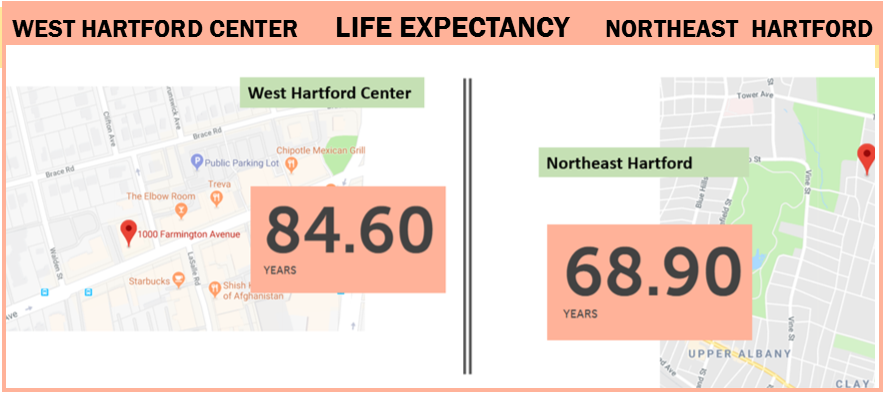
/by Arielle Levin Becker Hartford’s Northeast neighborhood is about four miles from West Hartford Center. Yet living in one place or the other can mean a 15-year difference in life expectancy.
That’s according to recently released data that identifies the life expectancy for nearly every census tract in the country, offering a stark illustration of the disparities that exist even between neighborhoods in the same city or region.
In Northeast Hartford, the life expectancy of 68.9 years is more than 11 years below the average life expectancy in Connecticut – 80.8 years. West Hartford Center tops that, at 84.6 years.
Similar patterns hold true across the state. There’s a nearly 14-year life expectancy gap between parts of Bridgeport and neighboring Fairfield. A baby born in Westport has a life expectancy that’s more than 20 years longer than a baby born in Northeast Hartford.
 There is variation within cities and towns. In New Haven’s Newhallville neighborhood, life expectancy is 71.7 years. In the neighborhood next door, Prospect Hill, life expectancy is more than a decade longer: 82.3 years.
There is variation within cities and towns. In New Haven’s Newhallville neighborhood, life expectancy is 71.7 years. In the neighborhood next door, Prospect Hill, life expectancy is more than a decade longer: 82.3 years.
Depending on the neighborhood, life expectancy in New London ranges from 69.8 years to 83.3 years (a 13.5-year difference), while in Norwalk, it ranges from 76.3 years to 87.9 years (11.6 years). Life expectancy in Torrington ranges from 71.6 years to 85.6 years – a 14-year gap.
The data comes from the United States Small-Area Life Expectancy Estimate Project, an effort of The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems, and the National Center for Health Statistics, which is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The numbers are estimates of average life expectancy at birth for 2010 to 2015 – that is, how long, on average, a person can expect to live.
“It is truly unsettling to see how small differences in geography yield vast differences in health and longevity. In some places, access to healthy food, stable jobs, housing that is safe and affordable, quality education, and smoke-free environments are plentiful. In others, they are severely limited,” Donald F. Schwarz, senior vice president, program at the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, wrote in a recent blog post. “Data can help us better understand the health disparities across our communities and provide a clearer picture of the biggest health challenges and opportunities we experience.”
All of this new data is consistent with a longstanding challenge in health in Connecticut: While Connecticut is among the healthiest states in the country, there are significant disparities in health outcomes by race and ethnicity – a sign that not everyone has the opportunity to be as healthy as possible.
Here are three examples:
- Babies born to black women in Connecticut are nearly three times as likely to die before turning 1 as babies born to white women, while among Hispanic mothers, babies are twice as likely to die in their first year.
- The rate of cancer deaths among black Connecticut residents was 9 percent higher than among white residents in 2016 – even though black residents were far less likely to be diagnosed with cancer.
- Hispanics in Connecticut were twice as likely to be uninsured than white state residents in 2016.
At the Connecticut Health Foundation, our work is centered on eliminating racial and ethnic health disparities and assuring that all Connecticut residents have access to affordable and high-quality care. We focus on ensuring that all state residents have access to health care coverage and a regular source of health care, as well as ensuring that the health care people receive is high-quality and connected to the many non-clinical factors that affect health.
The strategies that can help to eliminate health disparities will benefit everyone. They can also help move Connecticut closer to our vision of a state in which everyone – regardless of race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status – has the opportunity to be as healthy as possible.
_________________________
Arielle Levin Becker is Communications Director for the Connecticut Health Foundation, which focuses on improving health outcomes for people of color and ensuring that all Connecticut residents have access to affordable and high-quality care. Through public policy, grantmaking, and leadership development, the Connecticut Health Foundation works to make lasting changes that improve lives.




 The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.”
The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.” “Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.
“Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.

 The personal-finance website WalletHub compared the largest U.S. cities – including at least two from each state - across 31 key indicators of disability-friendliness. The data set ranges from wheelchair-accessible facilities per capita to rate of workers with disabilities to quality of public hospital system. The 31 indicators were grouped into three categories: Economy, Quality of Life and Health Care.
The personal-finance website WalletHub compared the largest U.S. cities – including at least two from each state - across 31 key indicators of disability-friendliness. The data set ranges from wheelchair-accessible facilities per capita to rate of workers with disabilities to quality of public hospital system. The 31 indicators were grouped into three categories: Economy, Quality of Life and Health Care.
 “Bridgeport has one of the lowest number of wheelchair accessible art, entertainment and recreational establishments per capita, and a large number of older buildings with little to no access for disabled residents," Gonzalez said.
“Bridgeport has one of the lowest number of wheelchair accessible art, entertainment and recreational establishments per capita, and a large number of older buildings with little to no access for disabled residents," Gonzalez said.


 A System of Professional Endorsement is Improving Connecticut’s Workforce
A System of Professional Endorsement is Improving Connecticut’s Workforce


 The
The 
 components of the overall score.
components of the overall score.

 Among the 10 largest state agencies in Connecticut, OEC’s goal is to keep the state’s children safe, healthy, learning and thriving. Through its innovative feedback efforts, the agency is acting on evidence that engaging providers and parents in policymaking yields better results. Officials said that the agency combined data from 1,700 family surveys, another survey shared with all providers in the state, and 400 community and provider meetings in order to build a draft plan to transform the ECE system in the state, which serves 200,000 children.
Among the 10 largest state agencies in Connecticut, OEC’s goal is to keep the state’s children safe, healthy, learning and thriving. Through its innovative feedback efforts, the agency is acting on evidence that engaging providers and parents in policymaking yields better results. Officials said that the agency combined data from 1,700 family surveys, another survey shared with all providers in the state, and 400 community and provider meetings in order to build a draft plan to transform the ECE system in the state, which serves 200,000 children.




























