Accelerating Efforts to Prevent Suicide in CT as Numbers Climb
/The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released a report this year which indicated that suicide rates nationally jumped by 25 percent since 1999, a finding that “shocked” even experts who believed the rate had been flat. Each year, more than 41,000 individuals die by suicide, leaving behind their friends and family members to navigate the tragedy of loss, according to the National Alliance on Mental Illness. Connecticut's rate, 9.7 deaths per 100,000, rose 20 percent during that time, and 49 states saw an increase, according to the CDC. Connecticut’s suicide rate, is ranked number 46 in the country.
Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death in the U.S. with one occurring on average every 13.3 minutes.
For every suicide, there are 30 people who made the attempt, Dr. James F. O'Dea, vice president of the Behavior Health Network of Hartford Healthcare, recently told the Meriden Record-Journal. The U.S. Health Resources & Services Administration reports that “approximately 45% of suicide victims had contact with primary care providers within 1 month of suicide.”
“Connecticut suicide rates may have no t have increased as much in comparison to other states, but isn’t the real question, ‘Why is it increasing at all?’” Luis Perez, president and CEO of Mental Health Connecticut, told The Hartford Courant earlier this year.
t have increased as much in comparison to other states, but isn’t the real question, ‘Why is it increasing at all?’” Luis Perez, president and CEO of Mental Health Connecticut, told The Hartford Courant earlier this year.
“It’s been well-researched that most people who die by suicide do so because they want the pain to stop — and they don’t see any other way,” Perez said. “Prevention is critical. Knowing the safe and right way to talk to someone who may have thoughts of suicide and letting people know they are not alone, that millions of people struggle with suicide ideation is key.”
According to the state Department of Public Health, approximately 31 percent of victims had a history of treatment for mental illness and 42 percent had previously attempted or thought about suicide or disclosed their intent to commit suicide. The CDC offers 5 steps to help someone at risk: 1. Ask. 2. Keep them safe. 3. Be there. 4. Help them connect. 5. Follow up.
The U.S. government’s anti-bullying website, stopbullying.com, points out that “many issues contribute to suicide risk, including depression, problems at home, and trauma history. Additionally, specific groups have an increased risk of suicide, including American Indian and Alaskan Native, Asian American, lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth.” The site indicates that “this risk can be increased further when these kids are not supported by parents, peers, and schools. Bullying can make an unsupportive situation worse.”
Matt Riley, Chief Operating Officer of the Connecticut-based Jordan Porco Foundation, recently told WTNH-TV that suicide is the second leading cause of death for Americans ages 15 to 24. One in ten college students and one in five high school students consider suicide. Young people considering suicide are most likely to talk to peers, so the Jordan Porco Foundation focuses on peer-to-peer outreach and awareness, with a series of successful program initiatives on college campuses in Connecticut and across the country.
In recent years, a new student-driven primary prevention program was piloted to help high school students develop positive coping skills and enhance protective factors in preparation for life beyond high school. Schools and organizations participating included Manchester High School, Immaculate High School in Danbury, Enfield Public Schools, Capital Preparatory High School in Hartford, Institute of Living in Hartford, Jewish Family Services in West Hartford, Wilton High School, Boys & Girls Club of Bristol, and Guilford Youth & Family Services.
Numerous organizations across Connecticut offer Mental Health First Aid, an 8-hour training to teach participants how to help someone who is developing a mental health problem or experiencing a mental health crisis. The evidence behind the program demonstrates that it helps trainees identify, understand and respond to signs of mental illnesses and substance use disorders. The course is often offered to participants free of charge.
https://youtu.be/jl87bmuCTdM
https://youtu.be/TT_HLG5FkKA


 The analysis, by the financial services website WalletHub, was based on 40 key indicators of livability, ranging from housing costs to school-system quality to restaurants per capita. The indicators were grouped into five categories – affordability, economic health, education & health, safety, and quality of life.
The analysis, by the financial services website WalletHub, was based on 40 key indicators of livability, ranging from housing costs to school-system quality to restaurants per capita. The indicators were grouped into five categories – affordability, economic health, education & health, safety, and quality of life.
 The survey revealed that residents are not satisfied with the current health care system: 80 percent agree or strongly agree that “the system needs to change.” When given more than 20 options, they focused on the high prices charged by industry players, citing most frequently as a “major reason” for high health care costs:
The survey revealed that residents are not satisfied with the current health care system: 80 percent agree or strongly agree that “the system needs to change.” When given more than 20 options, they focused on the high prices charged by industry players, citing most frequently as a “major reason” for high health care costs:
 The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.”
The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.” “Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.
“Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.
 The personal-finance website WalletHub compared the largest U.S. cities – including at least two from each state - across 31 key indicators of disability-friendliness. The data set ranges from wheelchair-accessible facilities per capita to rate of workers with disabilities to quality of public hospital system. The 31 indicators were grouped into three categories: Economy, Quality of Life and Health Care.
The personal-finance website WalletHub compared the largest U.S. cities – including at least two from each state - across 31 key indicators of disability-friendliness. The data set ranges from wheelchair-accessible facilities per capita to rate of workers with disabilities to quality of public hospital system. The 31 indicators were grouped into three categories: Economy, Quality of Life and Health Care.
 “Bridgeport has one of the lowest number of wheelchair accessible art, entertainment and recreational establishments per capita, and a large number of older buildings with little to no access for disabled residents," Gonzalez said.
“Bridgeport has one of the lowest number of wheelchair accessible art, entertainment and recreational establishments per capita, and a large number of older buildings with little to no access for disabled residents," Gonzalez said.

 The
The 
 Among the 10 largest state agencies in Connecticut, OEC’s goal is to keep the state’s children safe, healthy, learning and thriving. Through its innovative feedback efforts, the agency is acting on evidence that engaging providers and parents in policymaking yields better results. Officials said that the agency combined data from 1,700 family surveys, another survey shared with all providers in the state, and 400 community and provider meetings in order to build a draft plan to transform the ECE system in the state, which serves 200,000 children.
Among the 10 largest state agencies in Connecticut, OEC’s goal is to keep the state’s children safe, healthy, learning and thriving. Through its innovative feedback efforts, the agency is acting on evidence that engaging providers and parents in policymaking yields better results. Officials said that the agency combined data from 1,700 family surveys, another survey shared with all providers in the state, and 400 community and provider meetings in order to build a draft plan to transform the ECE system in the state, which serves 200,000 children.

 To assist patients who find themselves in this difficult situation, several states have passed legislation mandating a limit on out-of-pocket costs for medications. These limits can be applied in different forms, such as a per-drug cap or by mandating a copay-only structure in certain health plans. Those are just some of the areas of particular interest to
To assist patients who find themselves in this difficult situation, several states have passed legislation mandating a limit on out-of-pocket costs for medications. These limits can be applied in different forms, such as a per-drug cap or by mandating a copay-only structure in certain health plans. Those are just some of the areas of particular interest to 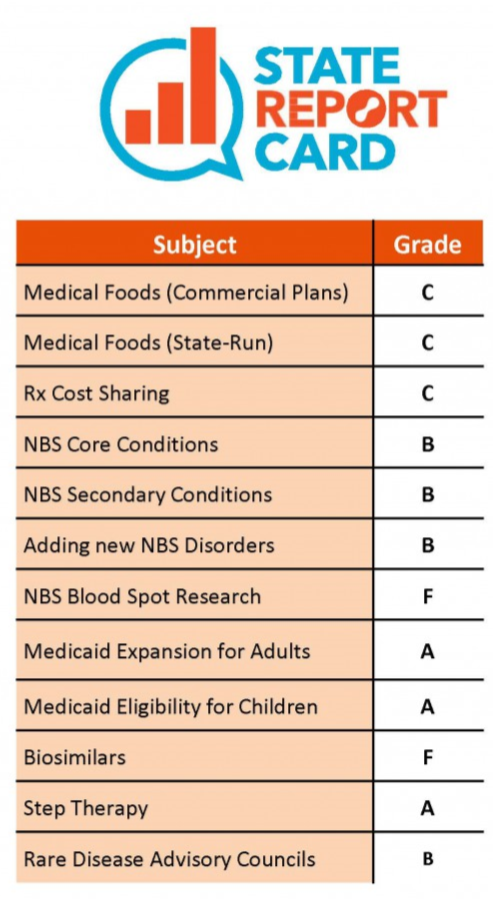



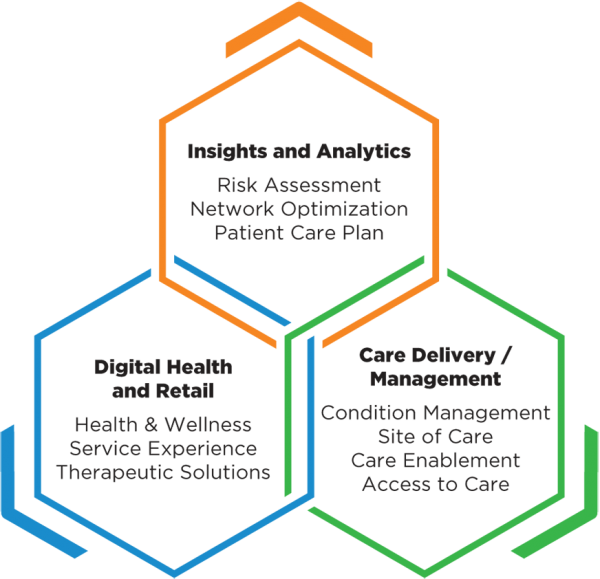 Companies in the portfolio, according to published reports, include Omada Health, a digital therapeutics company treating chronic diseases; Prognos, a predictive analytics company for healthcare; Contessa Health, a home-patient care service; Mdlive, which provides remote health consultations; and Cricket Health, a special kidney care provider.
Companies in the portfolio, according to published reports, include Omada Health, a digital therapeutics company treating chronic diseases; Prognos, a predictive analytics company for healthcare; Contessa Health, a home-patient care service; Mdlive, which provides remote health consultations; and Cricket Health, a special kidney care provider.



























