UConn Accounting Master’s Program Ranked in Nation's Top 10
/The University of Connecticut is getting high marks for its online master’s degree in accounting, earning a spot in the top 10 nationwide among online business programs ranked by U.S. News & World Report. UConn’s program, run by the School of Business, was ranked No. 8 among 213 online graduate business degree programs that the publication’s editors reviewed at colleges and universities nationwide. UConn’s online master’s of science degree in accounting (MSA) received particularly high scores for the credentials and training of its faculty, along with factors that measure student engagement such as retention, selectivity, graduation rates, and class sizes.
U.S. News also praised the program last year in a broader review of online business school learning initiatives, though it did not issue overall rankings then. The rankings were released this month.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, jobs for accountants and auditors are expected to grow by 16 percent between 2010 and 2020. The U.S. Department of Labor agency reports that “Stricter laws and regulations, particularly in the financial sector, will likely increase the demand for accounting services as organizations seek to comply with new standards. Additionally, tighter lending standards are expected to increase the importance of audits, as this is a key way for organizations to demonstrate their creditworthiness.”
The UConn program is designed to give students the knowledge they need for successful careers in public and private accounting, allowing current CPAs to expand their skill set and helping aspiring accountants meet the 150-hour educational requirement to seek CPA testing and licensing in most states.
“There are exciting innovations planned for the next year to continue keeping the MSA on the cutting edge. New tools will increase interaction and continue to develop strong online community ties,” says Amy Dunbar, the MSA program’s faculty director and an associate professor of accounting.
UConn’s MSA program started in 1999 and transitioned to a completely online program in 2003. It’s particularly popular with working professionals who want to boost their careers with advanced credentials. The average age of new entrants is about 28 years old, and the student body is split almost evenly between men and women.
New full-time students attend a one-week class in May at the Storrs campus to become familiar with the program, technology, instructors, and each other. They then take courses online during the following summer, winter, and spring semesters to complete the program’s requirements.
The course content is delivered through course-specific websites on a School of Business server. As a result, the activities do not have to take place at the same time for all students. That gives students flexibility to finish their work on their own timeframes, as long as it is completed by the assignment’s deadline. There are also several part-time options, including completing the degree over two summers or taking 10 courses over multiple semesters.
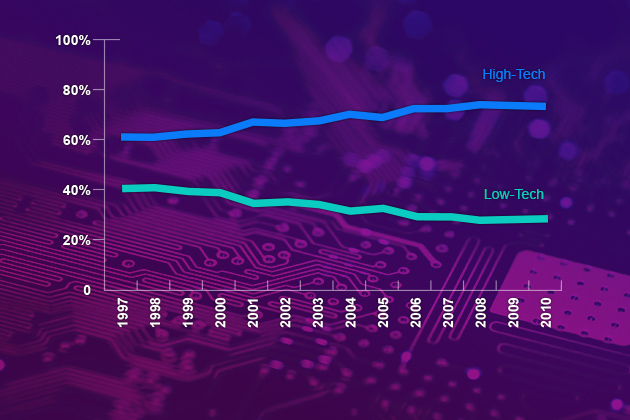
Recently, Robert Half, the world's first and largest specialized financial recruitment service, projected accounting salaries would grow 3.3 percent in 2013, while technology salaries will grow approximately 5.3 percent.
The UConn program has been recognized by the United States Distance Learning Association for best practices in the field, and it is accredited by the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB).



 that will inform the discussion:
that will inform the discussion: mic Development, notes a range of factors that could impact economic prospects, among them:
mic Development, notes a range of factors that could impact economic prospects, among them:
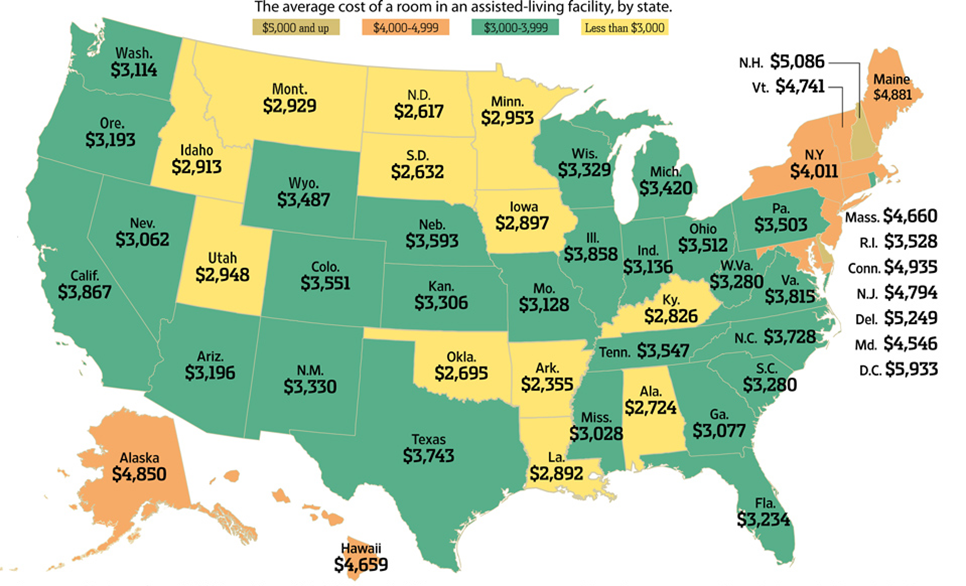
 correspondingly on Connecticut’s overall economy.
correspondingly on Connecticut’s overall economy.